Why a Specific Biostimulant Formula for Field Crops?
Field crops (cereals, oilseeds, protein crops and grain legumes) operate under high-volume scenarios, tight margins and significant environmental variability. In this context, a specific formulation that optimises nitrogen (N) efficiency, provides bioavailable sulphur (S) and supplies key micronutrients is critical to maintain yield and grain quality, while also improving the profitability of nutritional management. Terra-Sorb® granum meets this need with a combination of L-α-amino acids, sulphur, boron, zinc and molybdenum, designed to enhance nitrogen assimilation, mitigate stress and boost the translocation of photoassimilates, aspects that are particularly relevant in field crop systems.
The Physiological Basis: N and S, an Inseparable Pair
A sulphur deficiency negatively impacts nitrogen uptake and assimilation, limiting growth, yield and quality in species such as forage crops, peas, oilseed rape and wheat. Maintaining an adequate sulphur supply ensures the effective redistribution of nitrogen throughout the crop cycle, especially in cereals where grain nitrogen largely depends on the remobilisation of amino acids from vegetative tissues.
The Added Value of Sulphur as Ammonium Thiosulphate (ATS)
TerraSorb® granum incorporates ammonium thiosulphate (NH₄)₂S₂O₃ as its main source of sulphur, which is highly soluble, with 25% SO₃ in the product. Plants use thiosulphate as a source of sulphur, absorbing it through roots and leaves via the sulphate (SO₄²⁻) pathway; moreover, literature suggests possible direct assimilation routes for thiosulphate with lower energy cost compared to sulphate, resulting in metabolic efficiency under stress or limited resource conditions.
Beyond supplying sulphur, ATS has been described as an inhibitor of nitrification and urease at sufficient levels, which reduces nitrogen losses through leaching and denitrification and improves the efficiency of applied nitrogen (especially when combined with conventional nitrogen fertilisers). In field crop systems, this effect directly aligns with the goal of higher yield and better profitability per unit of nitrogen.
Strategic Micronutrients: B, Zn and Mo for Field Crops
- Boron (B): enhances pollen viability and mobilises photoassimilates during grain maturation; in soybeans, it supports nodule development and is associated with better oil and protein content in oilseed/protein crops.
- Zinc (Zn): involved in protein synthesis, enzyme activation, nucleic acid formation and carbohydrate metabolism; also linked to chlorophyll production and stress tolerance, factors that sustain growth and grain nutritional quality in cereals.
- Molybdenum (Mo): essential for inorganic nitrogen metabolism (nitrate reductase enzymes), photosynthetic efficiency and, in legumes, key for nodulation and biological nitrogen fixation (nitrogenase). Its supply is associated with yield improvements in the field (soybean and maize) and greater nitrate uptake in maize.
This trio of micronutrients works in synergy with sulphur and nitrogen, acting on enzymes and metabolic pathways that determine efficient nitrogen use, grain size and filling and production stability—decisive parameters in field crops.
L-α-Amino Acids: Complexation, Translocation and Resilience
The L-α-amino acids in Terra-Sorb® granum complex and facilitate nutrient translocation within the plant, improving foliar and root uptake of microelements and mitigating stress factors. Their use in a biostimulant aimed at field crops provides:
- Faster assimilation of micronutrients (B, Zn, Mo).
- Support for protein synthesis and C/N balance under high-demand conditions.
- Better response to thermal, water and oxidative stress—common situations in large-scale systems and treatments that may cause phytotoxicity.
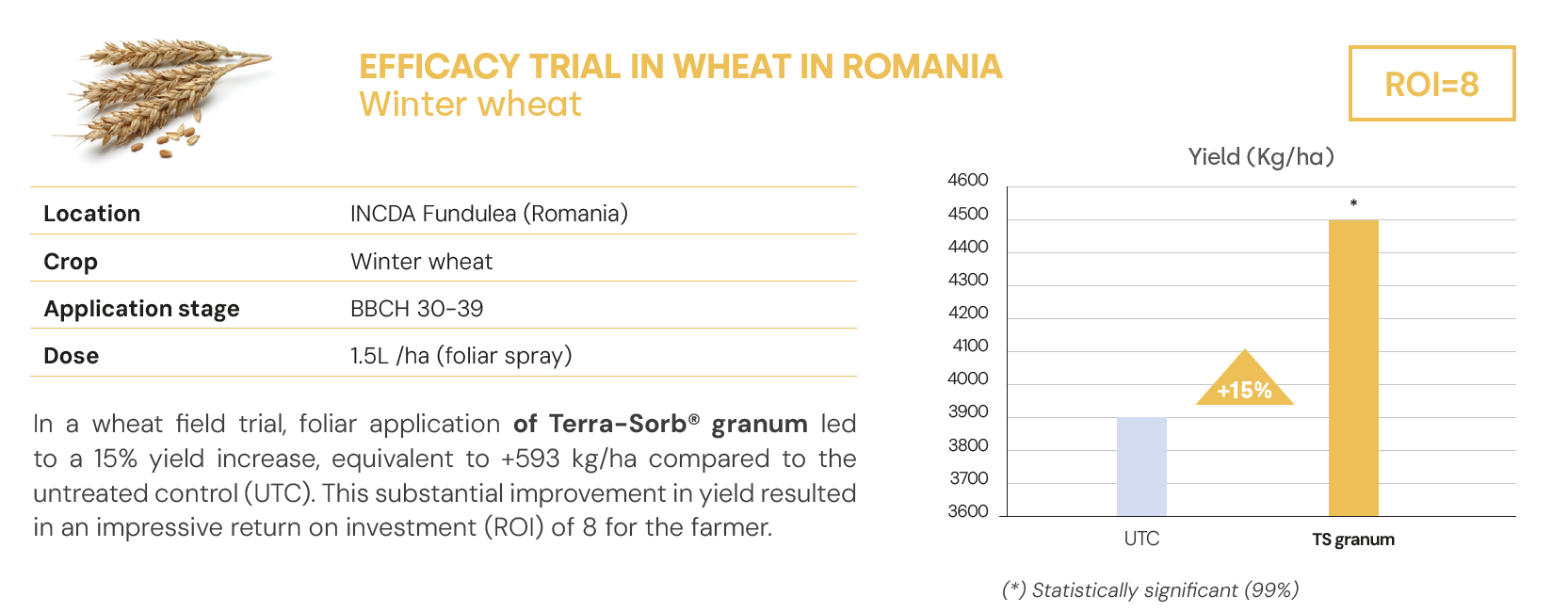
Conclusion
In field crops, where nitrogen efficiency, stress resilience and yield stability determine profitability, Terra-Sorb® granum delivers a specific formula that integrates sulphur as thiosulphate, L-α-amino acids and micronutrients B–Zn–Mo. This combination optimises nitrogen assimilation, improves translocation and reinforces key processes (enzymes, photosynthesis, protein formation and grain filling), maintaining yields and quality with compatibility in common crop protection mixes.

